Teradata Conversion Settings
Important Notice: Migration of Documentation Website
Please be advised that our documentation website is currently undergoing a migration to a new platform. To ensure you have access to the most up-to-date information, we kindly request that you visit our new documentation website located at:
Official Snowflake Snowconvert Documentation
For any immediate assistance or if you encounter any issues, please contact our support team at [email protected].
Thank you for your understanding.
General Conversion Settings
General Result Settings

Comment objects with missing dependencies: Flag to indicate if the user wants to comment on nodes that have missing dependencies.
Disable EWI comments generation (errors, warnings and issues): Flag to indicate whether EWIs comments (Errors, Warnings, and Issues) will not be generated on the converted code. The default is false
Generate XML-tags for SQL statements in Stored Procedures: Flag to indicate whether the SQL statements SELECT, INSERT, CREATE, DELETE, UPDATE, DROP, MERGE in Stored Procedures will be tagged on the converted code. This feature is used for easy statement identification on the migrated code. Wrapping these statements within these XML-like tags allows for other programs to quickly find and extract them. The decorated code looks like this:
Separate Period Data-type definitions and usages into begin and end Data-Time fields: This flag is used to indicate that the tool should migrate any use of the PERIOD datatype as two separate DATETIME fields that will hold the original period begin and end values, anytime a period field or function is migrated using this flag SSC-EWI-TD0053 will be added to warn about this change.
Input Code:
{% code title="IN -> Teradata_01.sql" %}
{% endcode %}
Output Code:
{% code title="OUT -> Teradata_01.sql" %}
{% endcode %}
Set encoding of the input files: Check General Conversion Settings for more details.
Use COLLATE for Case Specification: This flag indicates whether to use COLLATE or UPPER to preserve Case Specification functionality, e.g. CASESPECIFIC or NOT CASESPECIFIC. By default, it is turned off, meaning that the UPPER function will be used to emulate case insensitivity (NOT CASESPECIFIC). To learn more about how Case Specification is handled by SnowConvert check here.
To review the Settings that apply to all supported languages, go to the following article.
Session Mode Settings
This settings sub-page is used to indicate the Session Mode of the input code.

SnowConvert handles Teradata code in both TERA and ANSI modes. Currently, this is limited to the default case specification of character data and how it affects comparisons. By default, the Session Mode is TERA.
You can learn more about how SnowConvert handles and converts code depending on the session mode, check here.
DB Objects Names Settings
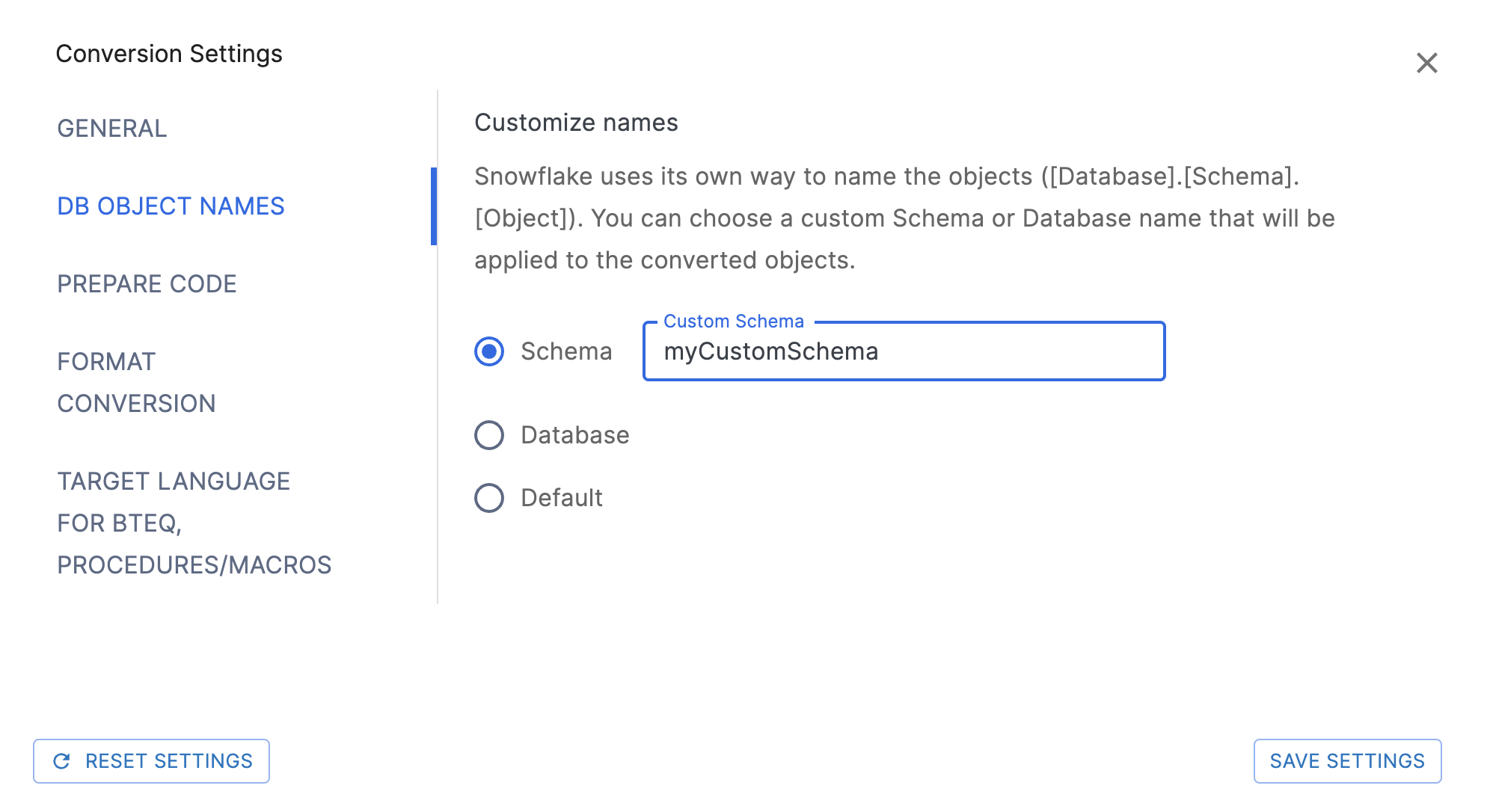
Schema: The string value specifies the custom schema name to apply. If not specified, the original database name will be used. Example: DB1.myCustomSchema.Table1.
Database: The string value specifies the custom database name to apply. Example: MyCustomDB.PUBLIC.Table1.
Default: None of the above settings will be used in the object names.
Prepare Code Settings
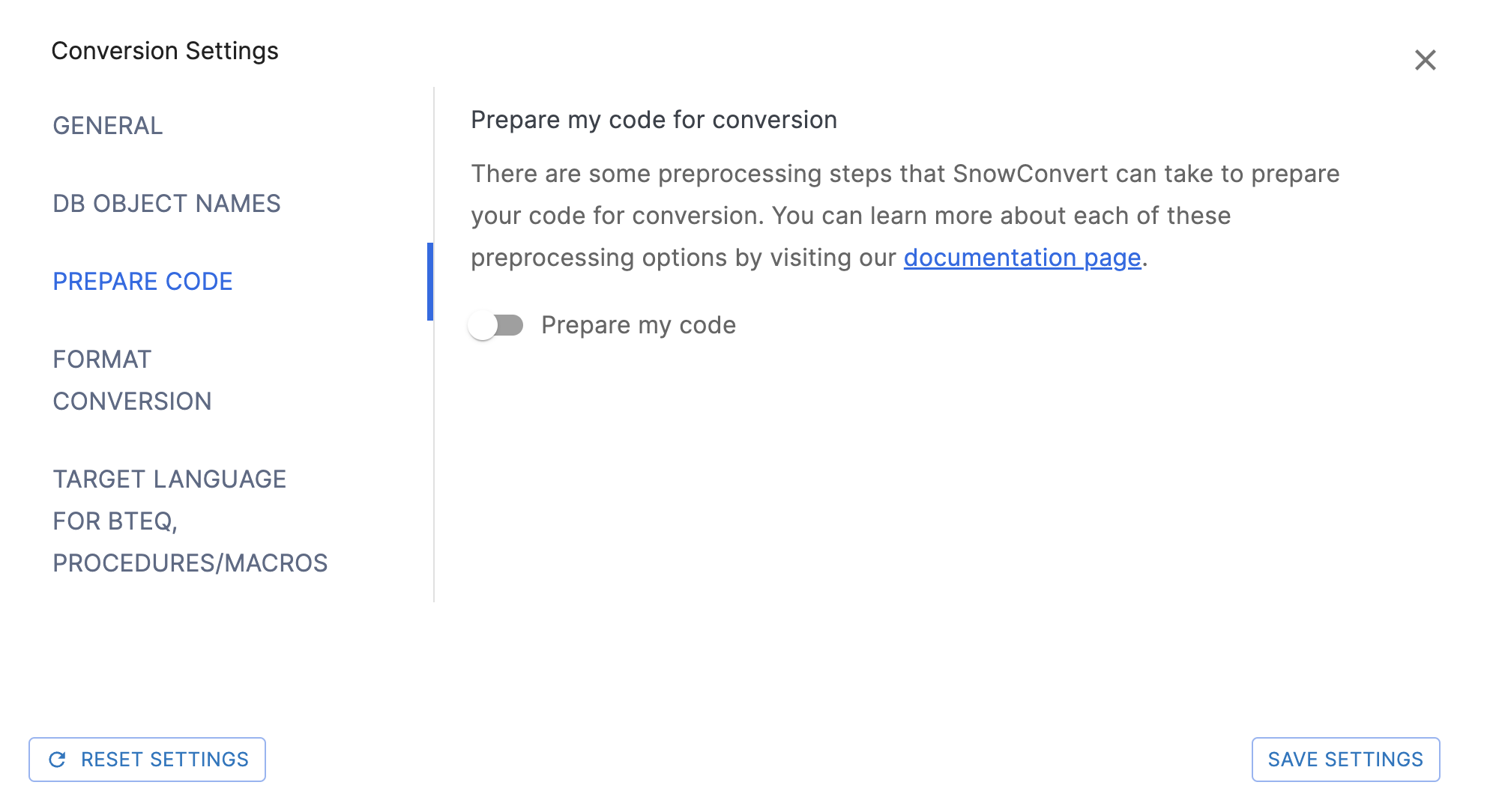
Description
Prepare my code: Flag to indicate whether the input code should be processed before parsing and transformation. This can be useful to improve the parsing process. By default, it's set to FALSE.
Splits the input code top-level objects into multiple files. The containing folders would be organized as follows:
Example
Input
Output
Assume that the name of the files is the name of the top-level objects in the input files.
Inside the "schema/database name" folder, there should be as many files as top-level objects in the input code. Also, it is possible to have copies of some files when multiple same-type top-level objects have the same name. In this case, the file names will be enumerated in ascending order.
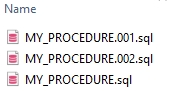
Only files with the ".sql", ".ddl" and ".dml" extensions will be considered for splitting. Other kinds of files like ".bteq" scripts will be copied into the preprocessed folder and will be categorized depending on the script extension but they won't be modified by the Split Task.
Requirements
To identify top-level objects, a tag must be included in a comment before their declaration. Our Extraction scripts generate these tags.
The tag should follow the next format:
<sc-top_level_object_type>top_level_object_name</sc-top_level_object_type>
You can follow the next example:
Format Conversion Settings
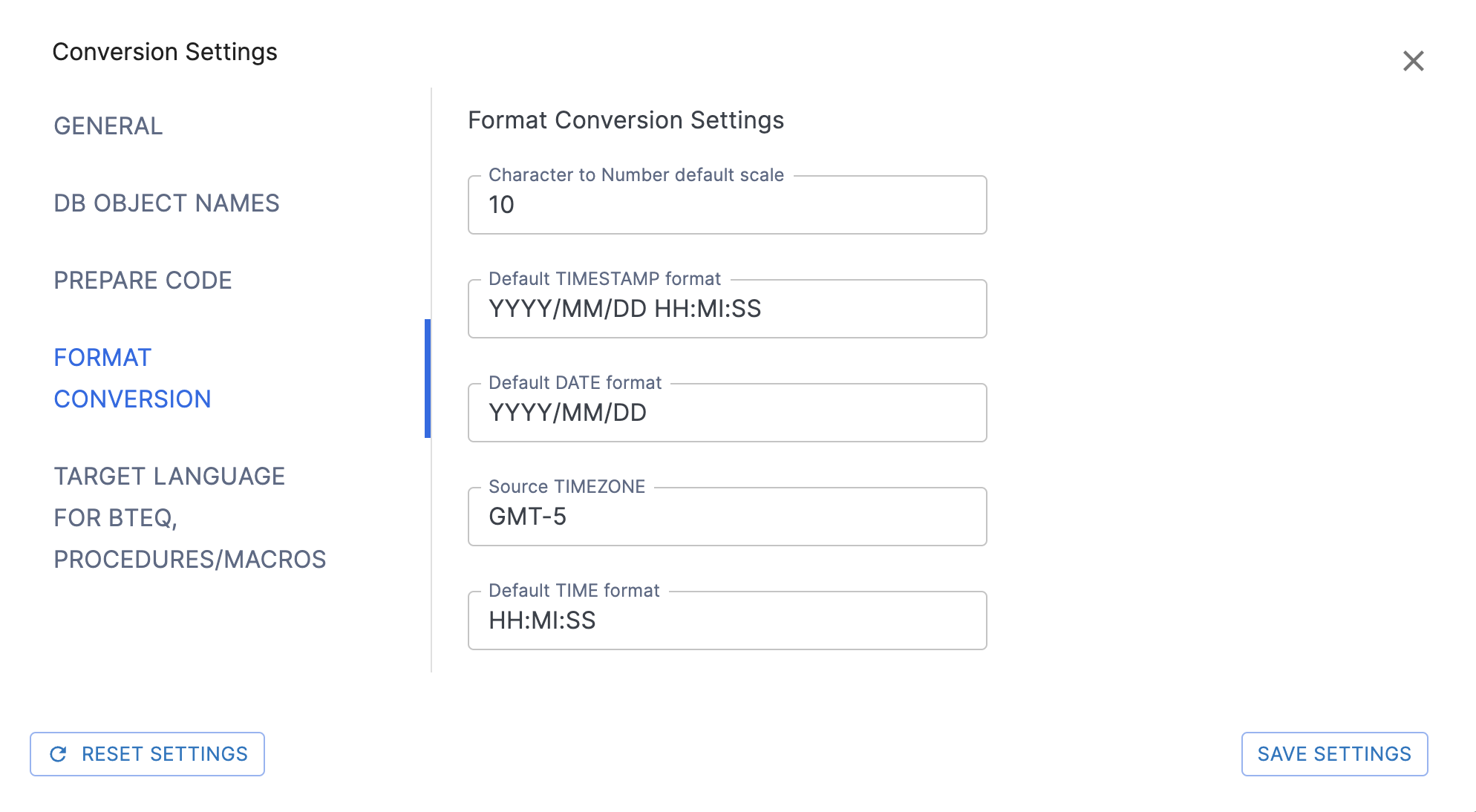
Character to Number default scale: An integer value for the CHARACTER to Approximate Number transformation (Default: 10).
Default TIMESTAMP format: String value for the TIMESTAMP format (Default: "YYYY/MM/DD HH:MI:SS").
Default DATE format: String value for the DATE format (Default: "YYYY/MM/DD").
Source TIMEZONE: String value for the TIMEZONE format (Default: "GMT-5").
Default TIME format: String value for the TIME format (Default: "HH:MI:SS").
Target Language for BTEQ, Procedures/Macros
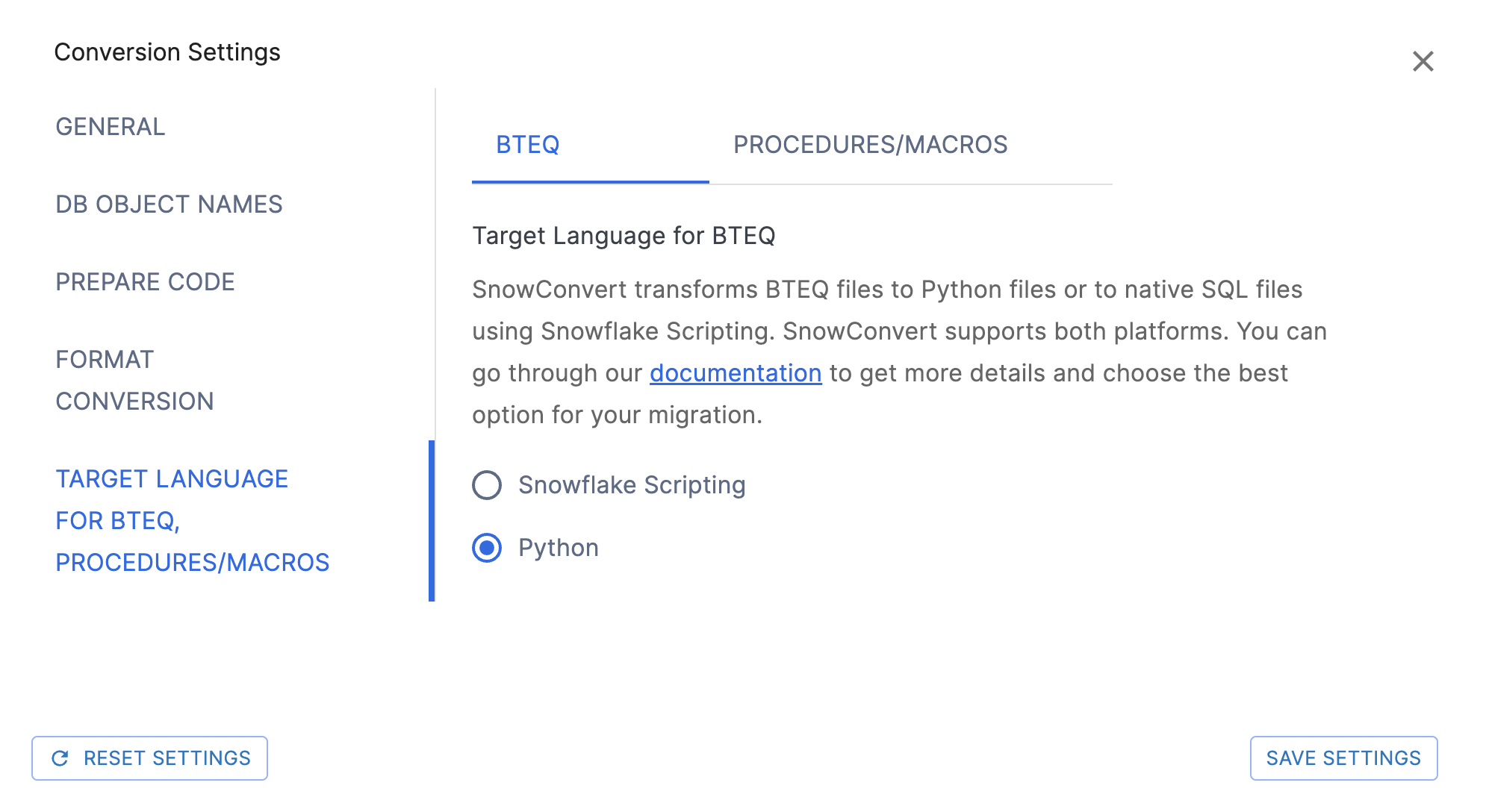
Specifies the target language to convert Bteq and Mload script files. Currently supported values are SnowScript and Python. The default value is set to Python.
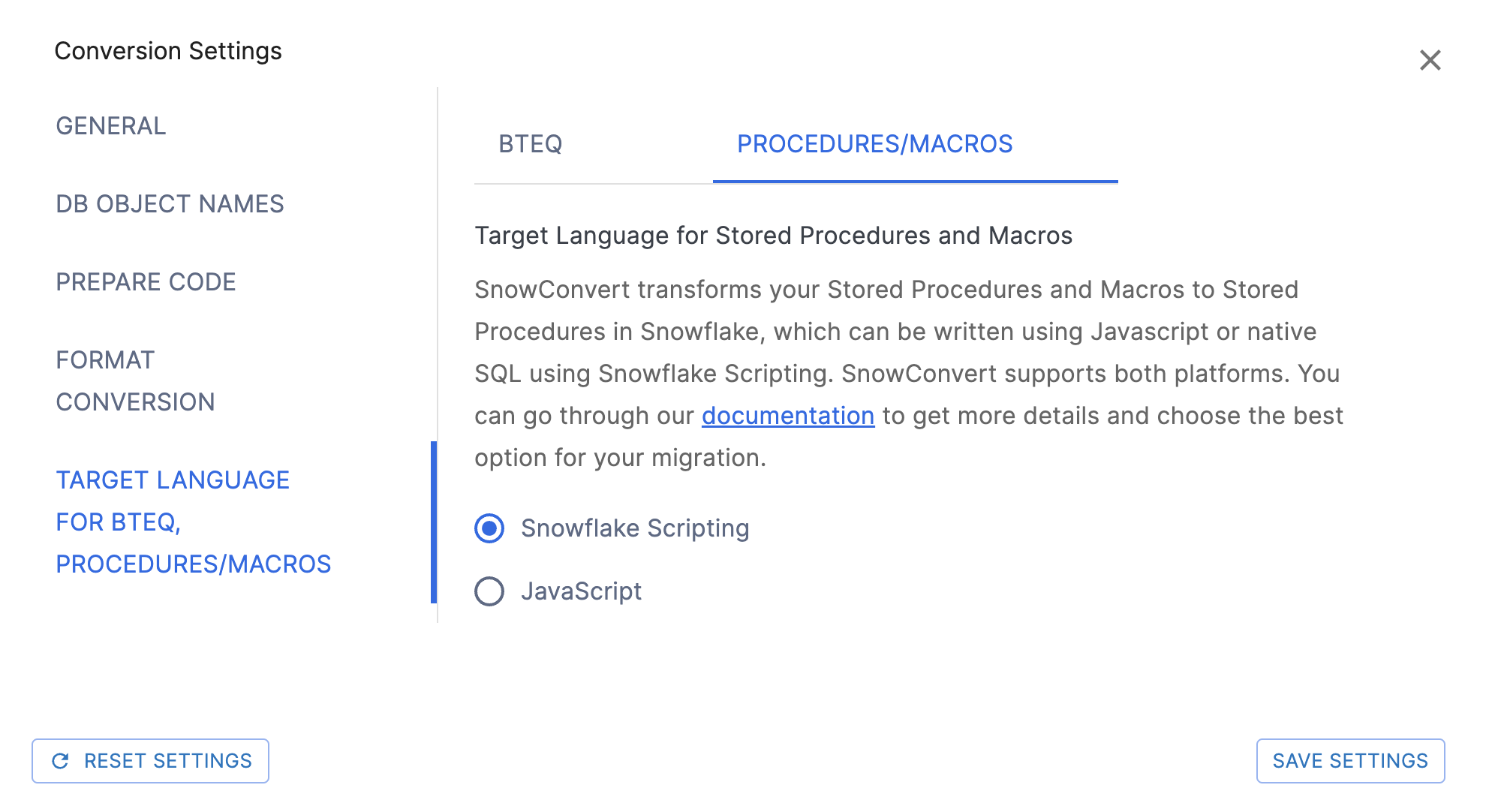
String value specifying the target language to convert Stored procedures and Macros. Currently supported are: SnowScript and JavaScript. The default value is set to SnowScript.
Reset Settings: The reset settings option appears on every page. If you've made changes, you can reset SnowConvert to its original default settings.
Last updated
